Precision agriculture- your best bet to improve farm productivity
What is precision agriculture?
Precision Agriculture is a farm management concept that revolves around the process of observing, measuring, and responding to various inter-and intra-field variability inputs for modern agriculture.
Popular definitions of Precision Agriculture (PA) or Site-Specific Crop Management (SSCM) describe the term as a technology-enabled approach to farming management that observes, measures, and analyzes the needs of individual fields and crops.
The goal of precision agriculture is to increase efficiency and productivity, reduce input costs, and improve environmental sustainability.
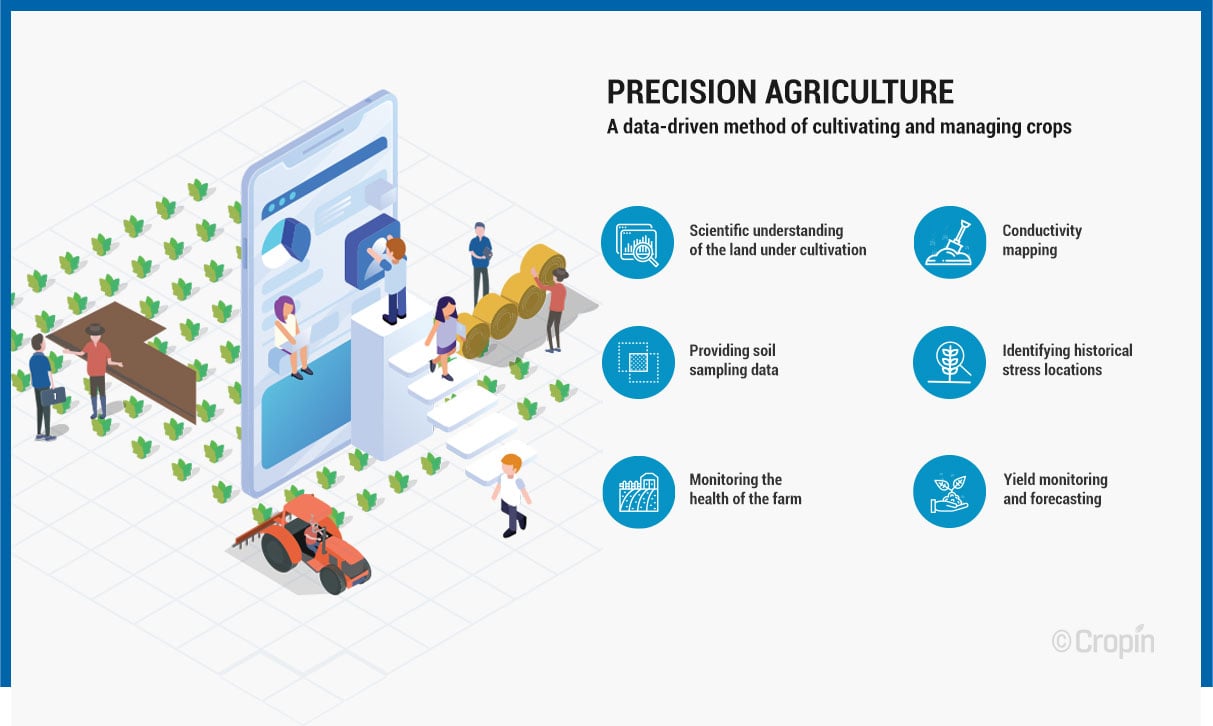
Precision agriculture and the farming revolution
But how is Precision Agriculture different from what farmers and agri-businesses have already been doing?
Looking to solve complex farm management challenges with precision agriculture?
Connect with our Ag-tech expert today to learn more!
Precision agriculture and predictive farming
Scope of precision agriculture
Advantages of precision agriculture
- A refined set of cultivation practices and choice of crops based on the suitability of land
- Elimination of volatility and risk
- Waste management
- Reduced production costs
- Minimum environmental impact
- Optimized use of fertilizers
- Water management with optimized irrigation practices
- Improved soil health
Making precision agriculture feasible through farm digitization
10 precision agriculture tools and technologies
2) Geographic information system (GIS)
- Fertilizers : VRT is used to apply fertilizers at different rates across a field, depending on the soil nutrient levels and crop requirements of each area. This can help farmers save on fertilizers and improve crop yields and quality.
- Pesticides : VRT is used to apply pesticides depending on the prevalence and distribution of pests and diseases across the field. This helps farmers control the amount of pesticides and reduce the risk of environmental pollution.
- Seeding : VRT is used to sow seeds depending on the soil characteristics and crop requirements of each area. This helps farmers optimize crop yields and quality.
- Navigation: Auto-guidance systems can help farmers navigate their vehicles and equipment around the fields with a high degree of accuracy, reducing the risk of errors.
- Row guidance : Auto-guidance systems can help farmers keep their vehicles and equipment on the correct rows, reducing overlap and skips.
- Equipment guidance : Auto-guidance systems can help farmers control and monitor the position and orientation of agricultural equipment such as planters, sprayers, and harvesters with a high degree of accuracy, improving implement performance and reducing errors.
- Record keeping and data analysis : Auto-guidance systems can record data on the location and movements of vehicles and equipment, which can be useful for record-keeping and analysis.
- Crop characteristics: Proximate sensors are used to measure crop characteristics such as height, biomass, and leaf area index. This information can be used to optimize crop management practices and improve crop yields.
- Soil characteristics : Proximate sensors are used to measure soil characteristics such as pH, nutrient content, nitrogen, and moisture content. This information can be used to optimize fertilization, irrigation, and other resource management practices.
- Pests and diseases : Proximate sensors are used to monitor the prevalence and distribution of pests and diseases in a field, in order to optimize control measures and reduce the risk of outbreaks.
- Data storage and management systems: Precision agriculture systems often generate large amounts of data, which needs to be stored and managed in a structured and efficient manner. This can be done using a variety of data storage and management systems, such as databases and cloud-based platforms such as Cropin Cloud.
- Data analysis and visualization tools : Precision agriculture systems often require the use of specialized software tools to analyze and visualize data in order to extract insights and make informed decisions.
Precision farming solution
Sustainable digitalization of agriculture with precision farming
The recent rapid digitalization has reduced the exhaustive paperwork in banks, hospitals, and most private and public sector organizations seem to diminish as their businesses move online. Digitization has reduced the manual work – which was time-consuming, error-prone, and inefficient – thus saving millions for corporations. Digitization of the economy has broken the barriers and has successfully curtailed the fear of tech dependency, especially among the farming community. Digitalization is slowly also revolutionizing the vast and complex Agriculture sector.
Precision agriculture and climate change
Precision agriculture- the road to sustainability
Precision agriculture- the road to sustainability
- Identify the best crops and hybrid seeds suitable for a particular area
- Work only on exactly identified areas to be replanted
- Take specific actions to provide the essential and optimum level of inputs (fertilizers and chemicals)
- Save time and cost and minimize the environmental impact of polluting soil and water
- Create maps for irrigation schedules and use ideal amounts of water to curtail wastage
- Anticipate pest infestations and diseases and take preventative measures before they destroy crops
- Apply weedicides and pesticides without harming biodiversity and killing non-target plants
- Harvest produce when they mature to meet consumer preferences and early enough to extend storage time
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What is precision agriculture?
What are some examples of precision agriculture technologies?
How does precision agriculture increase agricultural efficiency and productivity?
How does precision agriculture help reduce input costs?
How does precision agriculture help with environmental sustainability?
Author Bio
Prakhyath Hegde
Prakhyath Hegde is the Senior Vice President of Engineering at Cropin, the world's largest deployed AI platform for food and agriculture, bringing over two decades of experience in building hyper-scale software and AI-powered products. At Cropin, he is instrumental in leading the engineering for all platforms, including developing its multi-tenant, micro-services based Cloud & SaaS digitization platform. His work focuses on converging farm digitization data with advanced intelligence outputs from AI, ML, data science, satellite imagery, and remote sensing. A passionate problem-solver, Prakhyath previously held leadership roles at Samsung Research Institute and Viacom18, and has authored multiple scholarly articles and holds international patents.