‘Digital transformation’ has been creating a buzz in the agri-food sector for nearly a decade now. It has enabled private and governmental entities to apply innovations in digital technology to revamp processes and identify new business models.
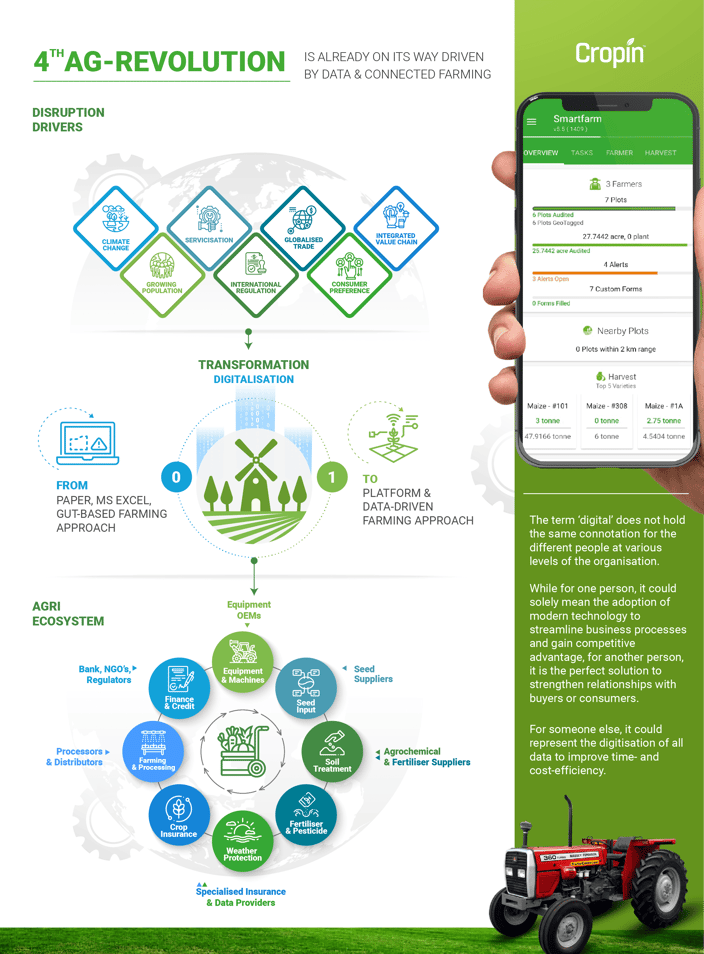
However, the term ‘digital’ does not hold the same connotation for the different people at various levels of the organization. While for one person, it could solely mean the adoption of modern technology to streamline business processes and gain competitive advantage, for another person, it is the perfect solution to strengthen relationships with buyers or consumers. For someone else, it could represent the digitization of all data to improve time- and cost-efficiency.
Nonetheless, for all that it is and could be, what role does ‘digital’ play in agricultural transformation? Why is it essential for agribusinesses to align their strategies with the envisaged digital transformation of the organization?
The Digital In Agriculture Today
One of the key elements that define ‘digital’ in agriculture is the use of technology. More commonly referred to as agriculture technology, or agritech, it encompasses the application of modern technologies in conjunction with the internet to reconstruct the practice of agriculture globally. Being digital has given large and medium organizations the power to unearth and analyze unprecedented volumes of agri big data, which has further enabled various stakeholders to create more value in the processes they oversee.
-
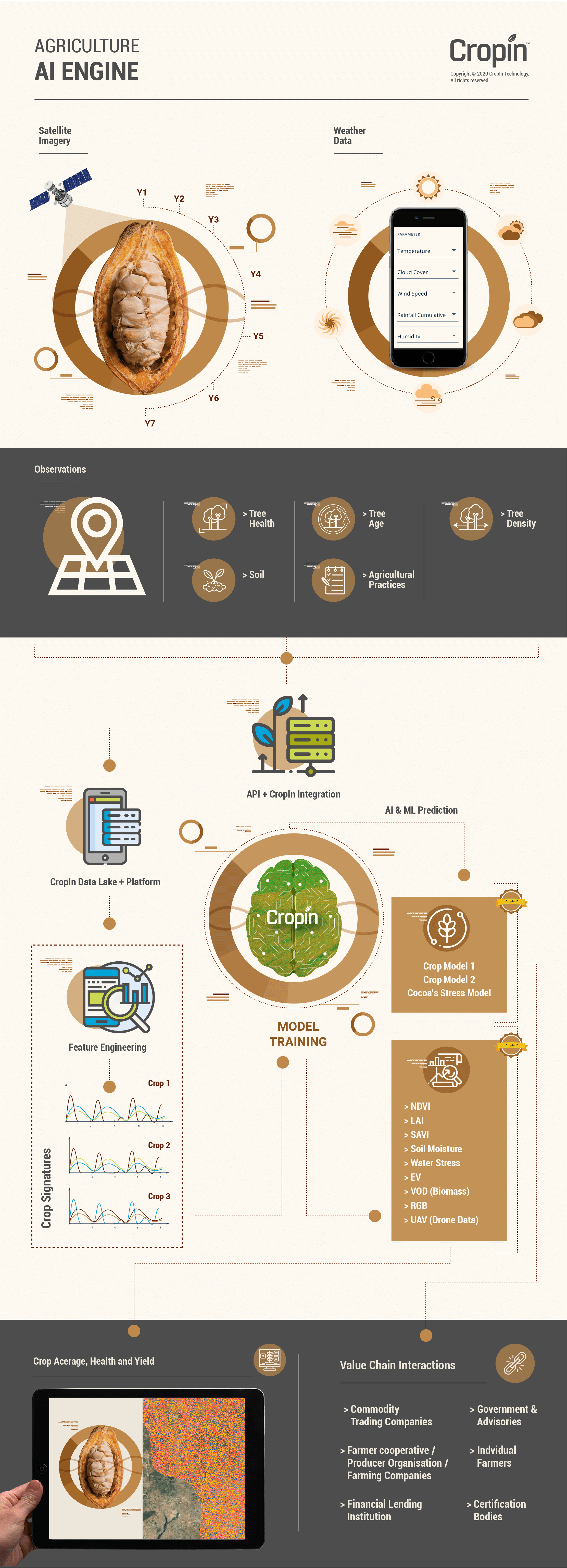
Farm-level data derived from a combination of sources, including mobile-based agriculture apps, sensors, drones, farm implements and machinery, robotic devices, and other IoT devices, makes it possible for producers to capture vital farm data round the clock. This data, when processed with satellite and weather-based information, allows crop producers to monitor the growth of crops in real-time, assess the performance of the farm plots, and estimate the output for each farm plot with a fair amount of accuracy.
-
Precision agriculture presents diverse opportunities for the use of artificial intelligence to optimize farm processes. It allows producers to translate raw agri data into actionable insights that help improve the quality and quantity of the harvest. AI is also empowering producers to choose the best crops and crop varieties for their region, and leverage farm automation to minimize the use of resources.
-
The digitalization of the entire process, from production and harvest to warehousing and distribution, is strengthening communications between the various stakeholders in the agri-ecosystem. Digitalization has also enhanced visibility along the supply chain for the different actors, making the process more transparent and highly efficient.
What Is the Impact Of Being Digital In The Agriculture Sector?
Increased productivity
The advent of Agriculture 4.0 has equipped food producers with an army of farm automation tools and data management solutions that empower them to boost resource and agricultural productivity. Farms that have adopted technological innovations have demonstrated a clear shift from the use of traditional, time-consuming processes to more advanced and cost-efficient operations. Additionally, the management can benefit from the use of digital agriculture to align their organizational strategies with the Sustainable Development Goals by ensuring more sustainable and resilient agri-food systems globally.
Enhanced farmer livelihood
Digital farming plays a vital role in understanding crop science and improving agronomic practices to yield better outputs. Scalable and cost-efficient solutions also facilitate large and medium enterprises to pass on a tried-and-tested package of practices to farmers, particularly in developing regions, to help them adopt more scientific methods of farming. The use of agri-technology improves farm productivity and helps reduce losses due to crop stresses such as pests, diseases, and unpredictable weather conditions. As a result, farmers can realize better profits at the end of each season. ICT solutions such as Cropin’s also enables producers to meet quality standards set by international certification bodies, which further makes it a possibility for farmers to fetch a premium price for their produce.
Better market linkage
Digital solutions support the virtual integration of multiple stakeholders, thereby providing producers with more direct access to agri and farm inputs, financial services, and commodity traders, among others. This, in particular, helps smallholder farmers overcome some of their challenges including inadequate intelligence on current commodity prices and other vital market information, the inability to negotiate payment, and lack of access to alternative buyers in the market.
Informed decision-making
Yet another remarkable benefit of adopting a digital agriculture system is that it provides users with accurate near-real-time data. An aggregate of farm and satellite-imaging-based intelligence provides actionable insights on productivity based on a wide array of growing conditions, thus permitting producers to plan farm operations better and manage resources more effectively. Additionally, intelligence gathered at various points along the supply chain also enables producers to understand market needs and drive crop production accordingly. Both private enterprises and governmental entities can leverage these insights to mitigate risks, improve crop management, and ensure minimal crop loss and food wastage.
Efficient policy-making and implementation
A sharp rise in mobile and internet penetration in India and numerous other developing nations has brought millions of farmers on the radar of policymakers. Digital innovations provide the opportunity for government entities to create a centralized database, wherein the details of farmers across each state or the entire country are made available. Seasonal data on crop production and plot performance also empower lending and insurance companies to identify potential risks, craft effective policies, and ensure their quick and thorough implementation. Having farmers register their details will also ensure that they get timely updates on agriculture-related schemes that are most relevant to them, to aid in their upliftment.

The use of big data analytics has had a far-reaching impact on several industries, including healthcare, financial services, retail and e-commerce, and even fraud prevention. Some of the key drivers of growth in the market for big data analytics include the immense volumes of complex data generated from increasing mobile data and cloud-computing traffic, as well as the adoption of advanced technologies across industries. A recent market research report forecasts that the digital transformation market will peak at $3,294 Billion by 2025, with a CAGR growth of 22.7% from 2019.
In agriculture, digitalization has paved the way for extensive transformation in the sector. Real-time monitoring of farm productivity combined with periodic satellite- and weather-based updates enable decision-makers to derive actionable insights on standing crops. This empowers them to handle operational difficulties more efficiently, combat climate and other environmental challenges with the help of scientific data, and optimize their supply chain activities based on timely updates. A report by the Business and Sustainable Development Commission indicates that for companies that design business models to tackle the varied challenges in the global food system, there exist business opportunities amounting to a total value of US$2.3 trillion. As discussed above, this value can indeed be realized by smarter farming practices powered by data-driven farming.
Starting with modernizing the way farming is carried out, creating better value for all the stakeholders in the ecosystem, to delivering nutritious food to people the world over, digital agriculture is encouraging broad-spectrum progress in the sector like never before. The transparency that modern innovations offer enables producers to manage supply and demand while also embracing the best practices for a sustainable future. The availability of rich data from different levels of food production and distribution is also capacitating the global R&D teams to increase operational efficiency both on and off the field, and to design agri-inputs that are capable of overcoming present-day challenges. Having set the stage for an explosion of cost-effective innovations in the sector, it is safe to conclude that this is just the beginning of the groundbreaking opportunities that lie ahead of us in the near future.






