Earth or soil is the primary provider of life on the planet. It is a natural resource without which there would be no food to drive the existence of living beings.
So, what will be the outcome when this provider is completely exhausted?
A practical solution to prevent the ensuing crisis is regenerative agriculture. Add to that digitization of such organic practices, and there you have a perfectly adequate and eco-friendly farming means. Farm owners still skeptical of utilizing this innovative and sustainable solution can learn about the farming process and its several benefits first. Here is a detailed guide.
What is Regenerative Agriculture?
Regenerative agriculture is a farming method that focuses on regenerating and revitalizing soil health through practices such as reduced tillage, cover cropping, and crop rotation. It refers to combining sustainable farming techniques to restore and boost the farmland’s ecosystem. It is a farming philosophy meant to heal the earth and regenerate natural resources, primarily soil, instead of exhausting them.
Historically, one of the most concerning issues in agriculture is soil depletion due to industrialized agriculture. The climate crisis in recent years has accelerated this. Rising temperatures and altered water cycles result in fluctuating precipitation patterns, affecting rainfall. Usage of intensive farming to compensate for such challenges further disturbs the ecological balance and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
Cropin encourages smallholder farmers to adopt agricultural practices based on resilience to curb the impact of climate change. This involves implementing sustainable farming techniques around water management, fertilizer usage, and other methods that may have lower—or even net positive—environmental and/or social impacts along with technological support. These farming techniques promote soil regeneration and improved soil health, thus minimizing nutrient-enriched topsoil depletion.

Photo by Jan Kopřiva
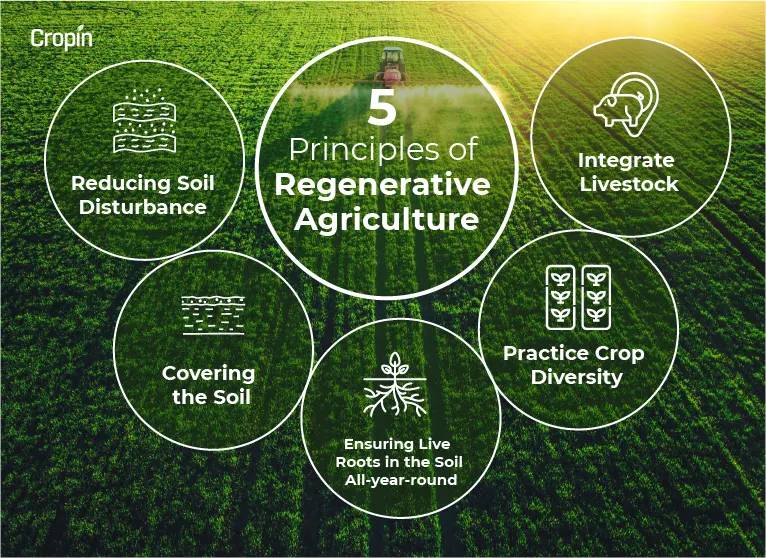
The 5 main Principles of Regenerative Agriculture
Here is a list of the five primary principles of regenerative agricultural practices.
1. Reducing Soil Disturbance
Industrial agricultural practices accelerate soil erosion. Therefore, the foremost requirement for soil regeneration is minimizing tillage and reducing soil disturbance. By reducing soil disturbance, regenerative agriculture aims to promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms and increase the soil's ability to retain water and nutrients. This can lead to increased crop yields and improved overall soil health. Additionally, regenerative agriculture helps to sequester carbon in the soil and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, making it an important strategy for addressing climate change.
2. Covering the Soil
A layer of green crops can protect the soil surface from harmful sun rays and frost and prevent rain from washing it away. It will enhance the soil’s water retention capacity, thus accelerating a better nutrient cycle. Regenerative agriculture places a strong emphasis on maintaining and building soil armor, which refers to the protective layer of organic matter on the surface of the soil. This layer helps to reduce erosion, retain moisture, and promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms. Some of the practices used in regenerative agriculture to build and maintain soil armor include
A. Cover cropping
This refers to planting a variety of crops between main crops to protect and improve the soil.
B. Reduced tillage
This helps minimize the disturbance of the soil to protect the soil structure and the microorganisms that live in it.
C. Crop rotation
This is the practice of rotating crops to different fields to reduce pest and disease buildup and replenish nutrients.
By maintaining and building soil armor, regenerative agriculture helps to improve soil health, increase crop yields, and build resilience to climate change.
3. Ensuring Live Roots in the Soil All-year-round
One of the key principles of regenerative agriculture is ensuring that there are live roots in the soil all year round. This is achieved through the use of cover crops, which are planted between main crops to protect and improve the soil. These cover crops are chosen to provide specific benefits such as fixing nitrogen, improving soil structure, or suppressing weeds. The continuous presence of live roots in the soil helps to improve soil health by
- Increasing the amount of organic matter in the soil
- Enhancing the soil's ability to retain water and nutrients
- Promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms
- Reducing erosion and promoting soil aggregation
- Improving soil structure, which leads to better drainage and increased water-holding capacity.
Planting living roots in the soil for the maximum time of the year provides adequate soil armor. These photosynthesizing plant roots will produce nutrition for the symbionts at the soil food web’s base. In turn, these organisms will ensure fertilizing services for current and future crops. By ensuring that there are live roots in the soil all year round, regenerative agriculture helps to build healthy, resilient soils that can support higher crop yields and better withstand environmental stresses such as drought and extreme weather conditions.
4. Practicing Crop Diversity
Another key principle of regenerative agriculture is practicing crop diversity. This means growing a variety of different crops on a farm, rather than relying on a single crop. Crop diversity can be achieved through the use of cover crops, crop rotation, and intercropping.
Monoculture can strip the soil of its nutrients and further promote erosion. Farming a diverse range of crops can ensure a balance of soil nutrients as different plants mineralize specific nutrients, which provides a balanced diet for the soil. Crop rotation, companion cropping, and cover cropping are a few ways to achieve it.
Crop diversity provides several benefits, including
- Reducing pest and disease buildup
- Enhancing soil health by adding different types of organic matter
- Improving soil structure by providing different root systems
- Improving nutrient cycling by providing different nutrient requirements
- Improving water infiltration and reducing erosion
5. Integrate Livestock
Regenerative agriculture also involves the integration of livestock into farming systems. This means raising animals such as cattle, sheep, pigs, or chickens in a way that is beneficial for the land, animals, people, and the environment.
Incorporating livestock grazing into your farming practices can amplify the benefits of the previously mentioned techniques. Grazing animals can help soil compost by dispersing seeds and breaking capped soil, hence facilitating gaseous exchange.
Other benefits of integrating livestock into regenerative agriculture systems include
- Improved soil health by adding organic matter and increased diversity of microorganisms through animal manure
- Enhanced nutrient cycling through the use of animal manure as a natural fertilizer
- Reduction in soil erosion by using grazing animals to trample and distribute plant material
- Improved water infiltration through reduced compaction and increased soil aggregation
- Providing a source of income and protein for the farmers and the local communities.
Integrating livestock into regenerative agriculture helps to create a more holistic, sustainable, and productive farming system that benefits both the land and the farmers.
Regenerative Agriculture Practices
Regenerative agriculture practices involve the following primary land use and farming practices:
1. No-till Farming
No-tillage farming practices are integral to minimizing soil disturbance. This technique involves seeding via disc planters or specialized drillers and pasture cropping. The latter requires sowing dormant annual plants in perennial pastures to promote diversification and improve productivity.
No-till farming is a method of growing crops without disturbing the soil through tillage. This can include practices such as planting cover crops, using precision farming tools, and applying fertilizers and pesticides with minimal soil disturbance.
2. Organic Cropping
Sustainable farming also involves using biologically-derived pesticides and fertilizers, like manure, animal compost, and plant wastes, as an environment-friendly practice. The ecological benefits of organic farming practices include reduced soil erosion, minimized leaching of nutrients into groundwater, and waste recycling, to name a few.
Organic cropping is a method of growing crops without the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). It relies on natural methods such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and the use of organic fertilizers.
Regenerative agriculture goes beyond organic cropping, it aims to build soil health, increase biodiversity, improve water management, and enhance ecosystem services. The practices of regenerative agriculture include organic cropping, cover cropping, holistic grazing management, agroforestry, and regenerative soil management. So regenerative agriculture is a broader term that includes organic cropping but also a more holistic approach to farming that focuses on regenerating the soil and the entire ecosystem.
3. Integrating Animal Grazing
Livestock integration can help in promoting soil fertility by eliminating pests and weeds. At the same time, it facilitates animal breeding in natural conditions.
Integrating animal grazing into regenerative agriculture practices can be an effective way to improve soil health and biodiversity. Grazing animals can be used to manage cover crops, control weeds, and improve soil structure.
Holistic management grazing, a management system that uses a planned grazing strategy to mimic the natural movements of wild herds, is one method of integrating animal grazing into regenerative agriculture practices. It involves rotating animals through different pastures, allowing each pasture to rest and recover before being grazed again. This can help to improve soil health and biodiversity by promoting the growth of diverse plant species, reducing erosion, and increasing the amount of organic matter in the soil. Other regenerative agriculture practices such as agroforestry, cover cropping, and regenerative soil management can also be integrated with animal grazing to create a more holistic, regenerative system.
4. Perennial Cropping
Planting perennial crops is a soil armoring technique to reduce erosion by carrier agents like wind and water, minimizing the need for chemical inputs and tilling operations. Perennial cropping is a regenerative agriculture practice that involves growing crops that come back year after year, rather than having to be replanted each year.
Examples of perennial crops include fruit trees, berries, and nut trees. This method of farming can help to improve soil health, increase biodiversity, reduce erosion, and sequester carbon. Additionally, perennial cropping can also provide farmers with a more stable and reliable source of income, as they do not have to invest in replanting crops each year.
5. Agroforestry/Silvopasture
Agroforestry and silvopasture are both regenerative agriculture practices that involve integrating trees and other woody vegetation into agricultural landscapes.
Agroforestry involves planting trees, shrubs, palms, and bamboo with extensive root systems with crops to protect the latter from strong winds and rain. It is the practice of growing trees and other plants together on the same land in a way that mimics natural ecosystems. This approach can include planting trees in rows along crop fields, intercropping, or even incorporating trees into livestock grazing systems. Agroforestry can help to improve soil health, increase biodiversity, reduce erosion, and sequester carbon.
On the other hand, silvopasture includes intentionally managing livestock, trees, and forage in the same productive agricultural landscape. Silvopasture is a specific type of agroforestry that involves integrating trees with pastureland for grazing animals. This approach can include planting trees in rows or groups within pastures or allowing trees to naturally regenerate within pastures. Silvopasture can provide numerous benefits, such as providing shade for livestock, improving forage quality, and improving soil health.
Agroforestry and silvopasture can be beneficial in regenerative agriculture practices. Both these practices diversify and sustain production for increased social, economic, and environmental benefits. They can help to improve soil health, increase biodiversity, reduce erosion, and sequester carbon. Additionally, it can help to provide farmers with a more stable and reliable source of income as they can diversify their production.
Read more- REGENERATIVE AGRICULTURE AND CONSUMER TRENDS
7 Benefits of Regenerative Agriculture
Regenerative agriculture is a farming method that focuses on regenerating and restoring the health of the soil. This approach to farming seeks to improve the overall health and productivity of the land, while also reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Some of the benefits of regenerative agriculture include
1. Improved soil health
Regenerative agriculture practices, such as cover cropping, no-till farming, and composting, can help to improve the structure and fertility of the soil. This can lead to increased water retention, improved nutrient cycling, and greater resilience to extreme weather conditions. Soil becomes visibly stickier with enhanced water retention, aiding in better root connectivity.
2. Increased biodiversity
Regenerative agriculture practices, such as agroforestry and silvopasture, can help to increase the diversity of plants, animals, and microorganisms in agricultural landscapes. This can lead to a more resilient ecosystem, with improved pest and disease management, and greater pollinator and beneficial insect populations. Agroforestry encourages afforestation and reforestation and helps transform degraded land into natural carbon sinks.
3. Biosequestration
Regenerative agriculture practices, such as cover cropping, composting, and agroforestry, can help to sequester carbon in the soil. This can help to mitigate the effects of climate change by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Eliminating or reducing soil tilling practices also reduces the release of carbon dioxide when the carbon sequestered in the soil gets exposed to the air. They increase the soil’s capacity to capture carbon, which contributes to the reversal of global warming.
Livestock grazing after crop harvest encourages the conversion of high-carbon residues to low-carbon organic manure. The natural manure distribution of managed rotational grazing also helps regenerate carbon in soils by storing the organic matter and capturing the methane and nitrous oxide, both of which are greenhouse gases that decomposing manure generates.
4. Reduced soil erosion
Regenerative agriculture practices, such as cover cropping, no-till farming, and agroforestry, reduce soil erosion. This helps improve water quality, protects against flooding, and maintains the productivity of the land.
5. Increased water retention
Regenerative agriculture practices, such as cover cropping, composting, and agroforestry, can help to improve the water retention of the soil. This can help to reduce the need for irrigation and increase crop yields during dry periods. The soil’s increased water retention facilitates groundwater recharge as well. Enriching soil quality counters the need to clear more land for agriculture, thus preserving existing biodiversity.
6. Greater resilience to extreme weather
Regenerative agriculture practices, such as cover cropping, composting, and agroforestry, can help to make agricultural systems more resilient to extreme weather conditions, such as droughts, floods, and heat waves. This can help to maintain crop yields and protect farmers' livelihoods.
7. Climate Smart Agriculture
Switching to organic fertilizers reduces the demand for their synthetic counterparts that require the burning of fossil fuels for their production. Further, the application of chemical fertilizers releases nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas with significantly higher global warming potential (265 times more by weight ) than carbon dioxide.
Promote Regenerative Agriculture with Cropin
Cropin’s intuitive platform is packed with a host of features that empower farming companies and other agribusinesses to encourage regenerative agriculture among farmers through applications like SmartFarm that simplify farm management.
These tools ensure efficiency and productivity in agricultural practices while striving toward fulfilling sustainability goals. The soil health data captured through IoT in agriculture can also help leverage regenerative agriculture by providing insights into how and when to increase organic matter and therefore achieve a better soil structure paving the path for climate-smart agriculture.
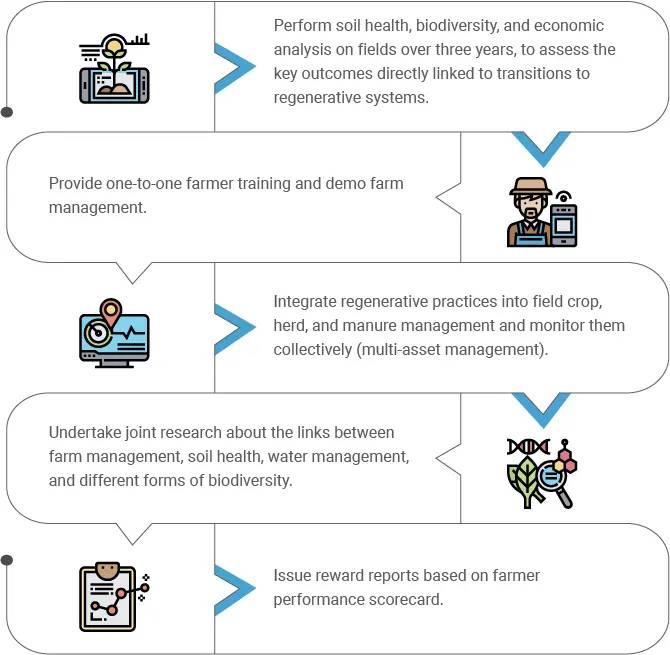
Adopting regenerative agriculture is a pressing priority for farming companies to save the planet and guarantee the survival of future generations. It also offers several economic benefits for enterprises and farmers via carbon offset markets.
Discover how you can achieve both with Cropin.







